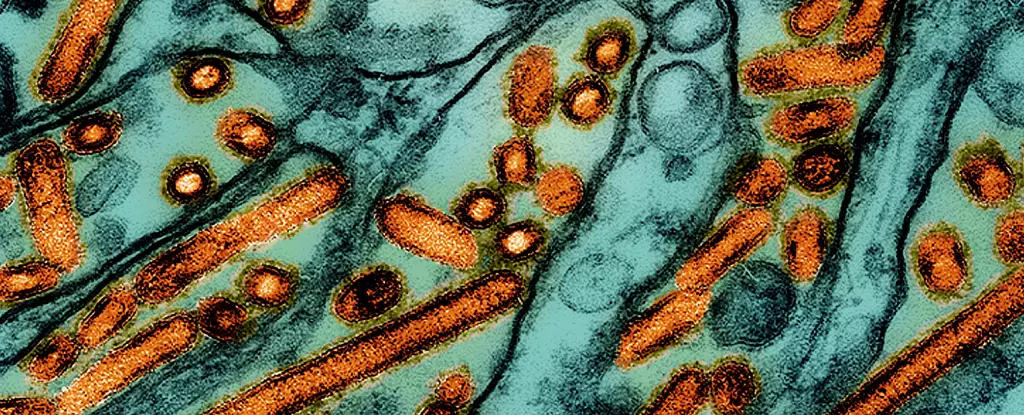
The emergence of a critical avian influenza case in Louisiana has thrown the United States into deep concern regarding the potential for a broader health crisis. As announced by health authorities, an elderly patient facing life-threatening respiratory issues due to H5N1 infection signifies a concerning escalation — the first severe human case linked to the ongoing bird flu outbreak this year. With the total number of infections now reaching 61, the fear isn’t only localized to Louisiana; it reverberates through the entire nation, particularly as states like California have declared emergencies to bolster their response capabilities.
This situation isn’t entirely without precedent. While most previous cases in the U.S. involved individuals exhibiting mild symptoms which allowed them to recover at home, the severity of the current incident marks a chilling shift. There were echoes of this magnitude of virulence in recent Canadian cases, bringing into question the effectiveness of existing surveillance measures and public health responses.
The H5N1 virus, responsible for the current outbreak, belongs to a particular genetic lineage known as the D1.1 genotype, with ties to avian populations across North America. This specificity is crucial for epidemiologists and public health officials attempting to understand patterns of infection and transmission. The identification of this genotype in both wild birds and domesticated poultry indicates a likely amplification of the virus within animal populations, creating numerous opportunities for spillover into human hosts.
As genetic testing illustrates affiliations between reported human cases and this genotype, the shadows of mortality loom large. Official statements from the CDC remind us that historically, H5N1 has had a disconcerting mortality rate, with fatalities linked to severe infections reaching as high as 50% in certain outbreaks. The existing body of research, therefore, suggests that authorities must be prepared for the grim possibilities that could arise from uncontrolled transmission dynamics.
The American Response and Preparedness
In recognition of the emergent threat posed by H5N1, California’s declaration of a state emergency is a proactive step. As Governor Gavin Newsom articulated, government resources must be directed swiftly to ensure thorough monitoring of both animal and human health. The expansion of monitoring demonstrated a shift to aggressive public health tactics aimed at curtailing the progress of the virus. Such measures are essential to catch potential outbreaks before they spiral out of control and secure the agriculture sector, which is vital to both the economy and the nation’s food supply.
Moreover, the announcement of fresh protocols requiring raw milk testing strengthens the framework for disease surveillance. Raw milk can serve as a vector for transmission, and ensuring that any positive cases are promptly reported will be crucial in safeguarding public health. This marks a shift in how agricultural products are handled and may require further recalibrating to minimize risks.
Despite heightened governmental action, experts have voiced concerns regarding the robustness of surveillance systems designed to detect avian-to-human transmissions. Rebecca Christofferson from Louisiana State University noted that a lack of rigorous monitoring might allow incidents to remain undetected. Further, the suggestion that asymptomatic human-to-human transmission could exist creates layers of complexity, increasing the uncertainty surrounding the spread of H5N1.
The comments from epidemiologist Meg Schaeffer emphasize a broadly held perspective that the avian flu is edging closer to a significant pandemic potential. Thus, the conversation should shift from reactive measures to proactive strategies reinforcing surveillance networks, public education campaigns, and community readiness in the face of this potential health crisis.
The Path Forward: Strategies in Research and Vaccination
Encouragingly, the U.S. government has been proactive in stockpiling vaccines against bird flu, readying itself for the worst-case scenario. Recent advancements with experimental mRNA vaccines offer promising avenues for combatting future viral outbreaks. Approaches that effectively protect experimental subjects like ferrets instill a sense of hope that similar successes can translate to human applications.
As the nation grapples with rising concerns surrounding avian influenza, the lessons learned from this outbreak will be pivotal. Developing robust public health frameworks, ensuring comprehensive surveillance operations, and expanding research into effective vaccines cannot be sidelined. The effort to combat H5N1 must not only focus on immediate threats but also pave a way for sustainable strategies addressing potential future health crises.